Soft packaging, labels, label seals, packaging date and time production date and consumption deadline, production lot, serial number, printing such as identification mark, labeling, allergy, brand name, logo, etc., trademark, marketing information, container material identification, printing system corresponding to the printing of variable information and RFID, packaged products for consumers, including the food processing industry, It has been proven in industries and industries such as pharmaceuticals, industrial goods, and distribution industries. If you have any problems with printing or displaying soft packaging, please contact us. For more information on the types of soft packaging, please refer here.
Date
Thermal printers have evolved from analog printing technologies such as hot stamps and roller coders, which are also used as thermal transfer printers (TTO), but began in the late 1970s as fax printers for business use. In addition, for the industrial industry, it has been widely used as a printer for date and bar code such as expiration date of production, consumption period due from running cost and on-demand printing and delicacy printing , but its contents, role or application of printing are expanding.
Barcode
There are over 100 types of barcodes in the world. They are composed of a combination of bars and spaces, and are codes that store data such as numbers and characters related to objects that can be read by a special machine.
It is used in various industries such as food, packaging, medicine, medicine, electronics, automobiles and aerospace.
JAN code (13 digits, reduced 8 digits), EAN code
This type is most commonly found. JAN is a bar code that displays the product code acquired by applying to the Chamber of Commerce.
EAN is a bar code for overseas distribution. It is displayed as a distribution code for products, and is used in systems such as sales information management (POS system), order management, inventory, and inventory management.
CODE39
Code 39 is a bar code mainly used for industrial product serial number labels and delivery documents for IEIAJ. In addition to the numbers, you can use English capital letters A ~ Z and some symbols. It is widely used as an industrial bar code. Unlike JAN and ITF, it supports non-numeric characters.
CODE128
Code 128 is a barcode that can display numbers, upper case letters, lower case letters, symbols, etc.
It is called Code 128 because it can barcode all 128 ASCII characters, and becomes smaller dimensions compared to other barcodes. Therefore, it is often used for labels of small electronic devices.
NW-7
NW-7 is a barcode often used in courier invoices and libraries. Although it is well known to call it Codebar, it’s called NW-7 in Japan. The reason is that one character consists of seven elements, and there are narrow elements (Narrow) and thick elements (Wide).
NW-7 is also called CODABAR. It is called NW-7 because it uses two types of widths, narrow (thin) and wide (thick), and consists of 7 elements, 4 bars and 3 spaces.
GS1-128 (formerly called UCC / EAN-128)
GS1-128 is a barcode standard based on Code 128 and displayed according to a certain rule.
Formerly called UCC / EAN-128. It is used for payment slips for convenience stores and labels for the distribution of pharmaceuticals and medical devices.
GS1-128 is standardized for product distribution based on CODE128. It’s also known as UCC / EAN-128. By using GS1-128, it can standardize not only the product code but also the information necessary for product distribution, such as the expiration date and lot number by specifying an identifier (AI) determined for each industry.
In addition, barcodes consisting only of numbers can be represented more efficiently and space-saving than ITF. It is used for medical supplies, medical devices, meat standard logistics, and payment slips for convenience store fee storage agents.
GS1 data bar (formerly called RSS)
GS1 Databar is a barcode that was formerly called RSS (Reduced Space Symbology), and it was renamed in February 2007.
Under the initiative of GS1, it is promoted for the purpose of standardization and tracking management of international distribution code (product number).
In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare is adopting and promoting the use as a new barcode that will replace the JAN code for pharmaceuticals.
GS1 data matrix
The GS1 data matrix uses gs1 application identifiers (AI:Application identifiers) to represent in a two-dimensional barcode symbology system called a data matrix. To distinguish it from a typical data matrix, it is called a GS1 data matrix.

GS1 data matrix encoding data and order
At the beginning of the data is FNC1, which is a symbol indicating that it is gs1 data. The rough order of the data after FNC1 is similar to other GS1 standard barcodes that use AI, usually in the order of product identification codes (GTINs) and attribute information. If the attribute information has a fixed length or variable length, precede the fixed-length data. If other data follows variable-length data, FNC1 is required as an item separator for variable-length data. The GS1 data matrix does not have a start or stop character, as used in GS1-128. In addition to numbers and alphabets, some symbols specified in the GS1 standard are available under ISO/IEC 646 international standards.

GS1 data matrix size
The size of the GS1 data matrix is determined by the module width. The module width is determined by the purpose of use, taking into account the creation of symbols and the ability to respond to the reader.
Square and Rectangle format
The GS1 data matrix has a square and rectangular format. The square format has 24 sizes ranging from 10 x 10 modules to 144 x 144 modules, and can encode up to 3,116 digits. On the other hand, the rectangular format has six sizes, ranging from 8×18 modules to 16×48 modules, and can encode up to 98 digits. Square formats are usually used because the square format has a wider range of sizes available and can encode large amounts of data.
Usage example
In the United States, Europe, and many other countries abroad, the GS1 data matrix has begun to be used for regulated healthcare products such as medical drugs and medical devices.
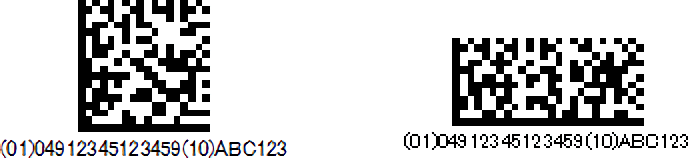
Traceability
These problems, such as misrepresentation, origin impersonation, increase in copied products, and contamination of foreign matter, have fundamentally shaken confidence in the product. In this situation, the role of printing and display is increasing as proof of the safety, trust, and security of products between manufacturers, suppliers, and consumers. As consumer’s demand for product safety becomes more stringent, printing and displaying have been challenged to prove quality and content, and their social responsibilities have become increasing. In addition, in the event of a product accident, if we know when, where, and how much was produced, it is possible to investigate the cause and recover the product quickly. In the world of consumer confidence in products, it is possible to minimize or prevent damage if there is a traceability mechanism that enables us to understand the movement (history) of each product through one or more stages of production, processing, and distribution. In addition to proving the contents and quality of printing and display, it is required to play a role as a history. It also makes it easier to build a traceability system that manages products by constructing code printing, variable printing, and using the code.
Food display
Change of food labeling method (April 1, 2020-)
The rules for printing and labeling on food have been standardized by the Food Labeling Act since April 2015. During transition period, fresh food labeling is applied one year and six months, and processed food and additives will be applied 5 years from April 1, 2020.
It is urgently required for all processed food companies, including production sites for prepared meals (such as prepared foods and lunch boxes).
The display items that are obligated by the Food Labeling Act are increasing such as nutrient component labeling, expiration date and shelf life (duration display), allergen labeling, small packaging for food, factory specific symbols, functionality display, display layout improvement etc.
labeling, small packaging for food, factory specific symbols, functionality display, display layout improvement etc.
In order to provide food products that meet the accurate food labeling, it’s necessary to consider the installation of priting system.
Raw material origin indication system of processed food (April 1, 2022~)
The food labeling standards were revised and enforced in September 2017, and it was obliged to carry out raw material labeling for all processed foods made in Japan.
Since the transition period of this system is until March 2022, it is necessary for you to meet the new raw material origin indication until then.
This is because consumers need the information of the raw material origin.
Raw material origin indication applies to all processed products except for imported products, and the raw material with the highest ratio of weight to raw material is subject to the indication, and in principle, it is national weight quasi-indication.
In addition, the place of production is displayed in case the target raw material is processed food,
It is also necessary to transmit the information of production area for business use.
In order to provide the information of raw material origin, it’s necessary to consider the installation of printing system.
Trademark / Brand Name
It is important to properly display trademark and brand names.
Local group trademark

The local group trademark system was created in April 2006 for the purpose of strengthening competitiveness by maintaining creditworthiness and revitalizing the regional economy by appropriately protecting regional brands.
Local business cooperatives, groups such as agricultural cooperatives, Chamber of Commerce, NPO can apply. They can receive a trademark registration consisting of “location name + product (service) name” for a product that has a close relationship with the area.
GI Japan geographical display

The Law on the Protection of Names of Specified Agriculture, Forestry, and Fishery Products (Geographical Display Act) came into effect in June 2015.
The purpose of this law is to protect the name of the product whose characteristics are linked with the area as intellectual property.
QRcode

Code printing on-demand thermal printer that can expands the use of QR code.
QR codes are useful for “convenience” in various sites. In addition to printed materials such as flyers and business cards, it is used in a wide range of products ranging from the living environment around us, such as payment systems, to businesses such as factories and distribution, and it is no longer an indispensable QR code for daily life.
QR code model 1
The first QR code, the maximum version is 14 (73×73 cells) and can handle up to 1167 digits.
QR code model 2
It is the code which improved model 1 so that it can read smoothly even if the code becomes distorted. Even if the code is printed on a curved surface or the code is distorted at the angle at the time of reading, the alignment pattern placed inside the code can be read well. The maximum version is 40 (177 x 177 cells) and can handle up to 7089 digits.
Micro QR code
A major feature of micro QR code is that there is one cut-out symbol. In the case of QR code, because the cut out symbol is arranged in three corners, it requires a certain size. In addition, a margin of at least four cells was required around the code in the QR code, but in the case of a micro QR code, it is sufficient to secure a margin of two cells. This structure allows micro QR codes to be printed in a smaller space than QR codes.
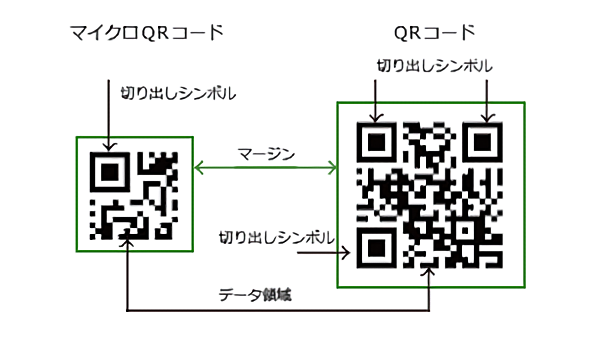
Micro QR codes do not have much data to store. (up to 35 characters in number) Compared to QR codes, data can be stored efficiently against code size, so the code doesn’t get that much bigger as the amount of data increases.
Micro QR code has four versions from version M1 to M4. Even the maximum version of M4 has less data to store than QR code version 1.
iQR code
It is a matrix two-dimensional code that can read the position and size of the code easily. You can generate a wide range of code, from codes that are even smaller than traditional QR codes and micro QR codes, to large codes that can store more data. It is also the smallest QR code that can be used in a wide range of fields because it can be rectangular or printed with front and back inverted, black-and-white inverted, and direct part marking.
RFID
It is a system to read and write RF Tag data using radio waves without contact. It is possible to scan the tag all at once by the electric wave. As long as the signal reaches, it can be read even if the tag is far away. In the operation with the bar code, scanning the Tag one by one with the laser.
RF Tag
RFタグは、メモリが内蔵された記憶媒体です。数ミリ程度の大きさですが、メモリには電子情報を入力したり消去したり書き換えたりすることが可能で、これらは電波(電磁波の一種)を用いて行います。RFタグはICタグと呼ばれることもあります。また、バッテリーが内蔵されている「アクティブ型」もありタグから発信される電波をリーダライターが受信することで情報をよみとります。
Reader Writer
RFタグに入力されている電子情報を読み取る機器です。読取は、リーダをRFタグのほうにかざしてスイッチを押すだけで、読み取り(スキャン)は終了します。RFIDは、電波を使って情報の保管と引き出しができるシステムです。すでに日常生活に浸透していて、交通機関で使われているSuicaやプリペイド型電子マネー楽天EdyなどもRFIDを利用しています。
POSレジの効率化
一括スキャンすることによってレジ作業が効率化するため、1人の客にかかる会計時間を削減することができます。
在庫管理作業の効率化
「いまの在庫」が常にリアルタイムで把握でき発注業務もスムーズに進みます。
賞味期限・消費期限の管理
RFタグには食品の賞味期限や消費期限のデータを入力することもできます。すべての商品にRFタグを貼り付ければ、それらの消費期限・賞味期限をパソコン上で把握することができるので賞味期限が近づいた商品を管理しやすくなります。食品廃棄を減らし利益向上につなげることも可能になります。
製造小売業での生産から消費者販売まで一括した管理
製品や食品を製造するメーカーがRFIDを導入すれば、生産から販売まで1個の商品・食品を追跡することができます。トレーサビリティを実現することができます。すぐに原因を追究でき、改善に取り組むことができます。責任の所在が明らかになるので、メーカー、卸会社、運送会社、販売会社などのバリューチェーンの関係各社が無駄なく対策を講じることが可能になります。また、これまで製品を「ロット」で管理するしかありませんでしたが、RFIDによって製品を「1個ごと」に管理・追跡することが可能になり、製品管理に関わる労力を減らすことも可能になります。
RFIDの周波数
日本国内ではLF帯(中波帯):120~130kHz、HF帯(短波帯):13.56MHz、UHF帯(極超短波):900MHz帯、マイクロ波:2.45GHz帯が主に使用されています。LF帯(中波帯)、HF帯(短波帯)、マイクロ波:2.45GHzは世界的にほぼ同一規格になっていますが、UHF帯(極超短波)は国によって規格が異なります。
バーコードとタグ
ID、個体識別の分野では、RFタグ(RFIDタグ、ICタグ、無線タグ)はバーコードと比較されますが、バーコードの利点はコストです。印字できる印字エリアがあれば大量に安く個体の識別が行えます。また社会インフラとして整っており、現在は商品にはバーコードがつけられ、各店舗でバーコードリーダーが普及しています。しかし、バーコードは一定の貼付エリアが必要であり、かつ汚れに弱い、データ量が少ない、データの書き換えができないといった点があります。QRコードやタグがそれらの欠点を補い、更に利用用途により選択の幅が広がっています。
RFIDとバーコードの違い
| RFID | バーコード | |
|---|---|---|
| 通信距離 | 長い(~数十m以上) | 短い(数cm) |
| 同時読込 | ◯可能 | ×不可能 |
| 記憶容量 | 大 | 小(QRコード 中) |
| 書込み | ◯可能 | ×不可能 |
| 汚れ | ◯強い | ×弱い |
| コスト | △高い | ◯安い |
IoTとタグ
IoT とは Internet of Things の略で、モノのインターネット、つまり、いろいろなモノがインターネットにつながり、クラウドにデータが保管されることをいいます。電子タグ(RFID)はIoTにおいて、センサーなどと同じように情報を収集する仕組みの一つになります。例えば、アパレル業の場合、商品である服に電子タグをつけることで、工場での製造工程から、物流、小売、販売までの全てのサプライチェーンのトレーサビリティ(製品の管理)を行うことができます。 今、どこに、何が、どれくらいあるか、どういったお客様が買われたのか等の全ての情報はクラウドにビックデータとして蓄積されます。アパレル会社は、それらのデータをもとに、売れ筋商品の生産、流通在庫の低減、オペレーションの効率化、新商品の開発などに活用しています。
Standard
JASマーク
JASマークは、しょうゆや木材などに表示され、広く知られているいわゆる丸JASマークと、「地鶏肉」や「熟成ハム」など、特色のある規格のマークに大きく分けられます。
この特色のある規格のマークを統一し、国内、海外市場において特色をアピールできる新たなJASマークが決定されました。
国内外において、「信頼の日本品質」を一目でイメージしていただくため、日本を象徴する「富士山」と、日の丸を連想させる「太陽」を組み合わせ、シンプルにデザインしました。それぞれの規格の内容を富士山の裾野部分に記載します。なお、配色の指定はしない予定です。
【参考】 新JASマーク

有機JASマーク
(農水省ページより抜粋)
有機JASマークは、太陽と雲植物をイメージしたマークです。農薬や化学肥料などの化学物質に頼らないで、自然界の力で生産された食品を表しており、農産物、加工食品、飼料および畜産物に付けられます。
【参考】 参考有機食品の検査認証制度
Inquiry about printing test
Please feel free to contact us if you need a printing test for your consideration.
